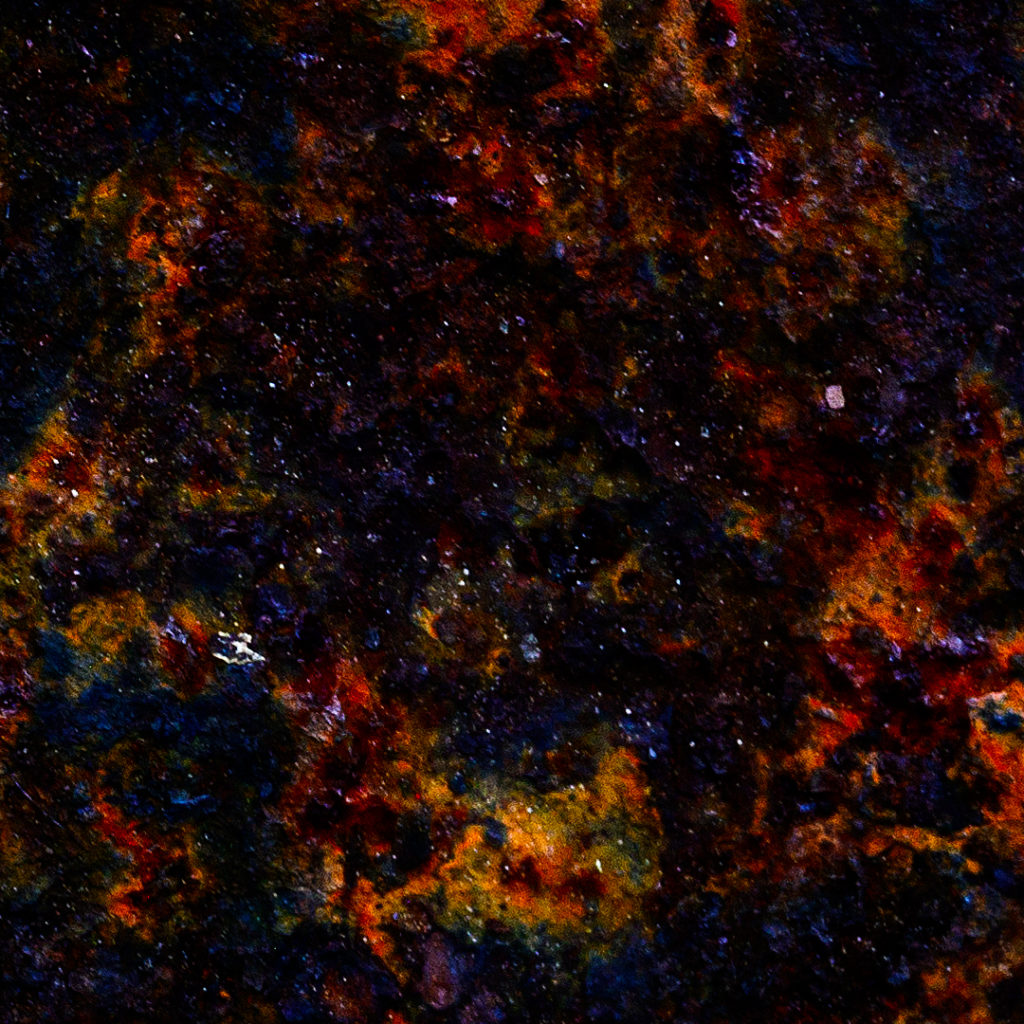
We all have biases that affect how we see the world. As a photographer, one of the things I strive to learn is to see beauty in the world even when it’s not obvious. For example, my bias may be to see the obviously ugly, natural appearance of something, but I will choose to seek to see what else is there. This is perhaps a sort of deliberate bias, but it often reveals unexpected beauty.
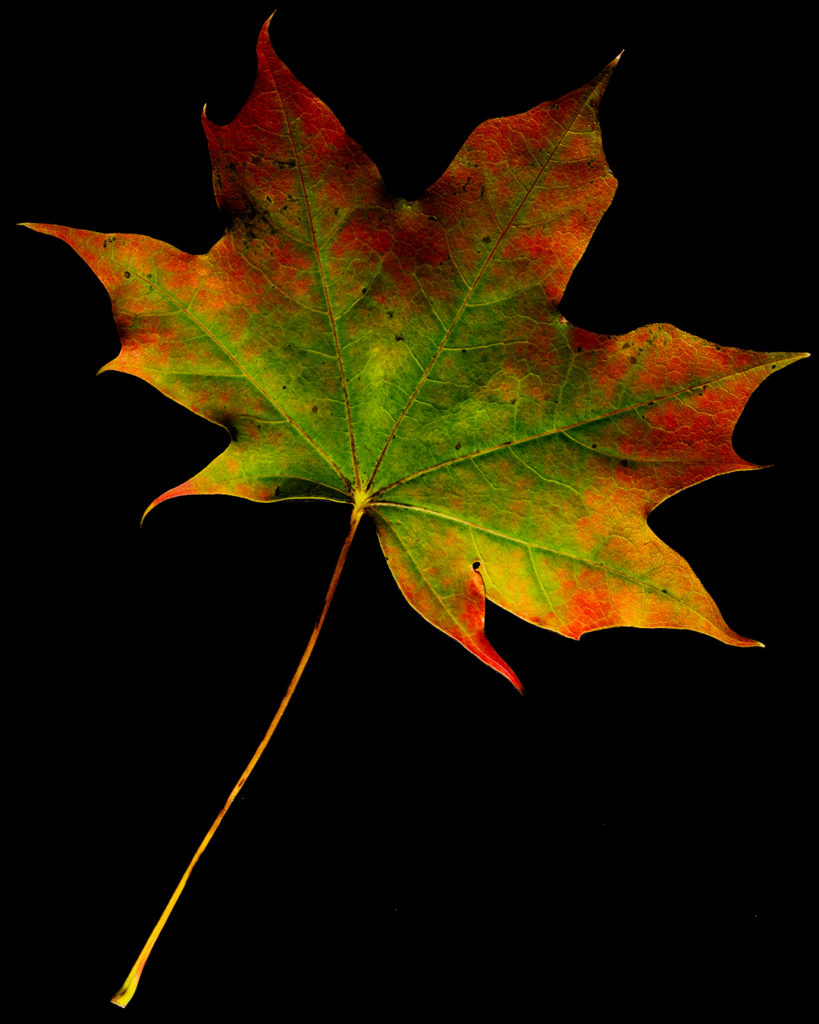
Take, for example, this photograph. To me, it looks like a picture of deep space, with glowing gas clouds, fields of stars, and layers of detail that recede into infinity.
In reality, however, this is simply a rusting metal plate. I looked for and found a different aesthetic by refusing to limit myself to what I thought rust should look like and chose to see it a different way. Of course, it did take some processing to make it look like this, but the point is that I was deliberately trying to look beyond my bias of ugliness to find some beauty, and this resulted.
This tendency goes beyond photography, of course, and applies to pretty much all our perceptions, the ways in which we see the world around us. It even applies to scientists who are deliberately trying to extend knowledge beyond current understanding, especially in fields with high uncertainty. It’s common for individuals to start with a proposed answer and attempt to find supporting proof, rather than start with an array of options to narrow down. It’s even less common for people to deliberately try to disprove their preferred understanding.
An example of a scientific domain that reflects this challenge is research into the nature of consciousness. Consciousness is so poorly understood and is such a different phenomenon that it challenges existing views of physicalism (the idea that reality consists of only physical entities). As such, scientific research into it is subject to biased thinking because some approaches to explain it, even though not based on any religious ideas, sound religious to some people and so get immediately rejected.
I’ve written before about how consciousness is a challenging topic and how photography may help. Perhaps one specific possibility is that it can be used to address bias by helping us learn to see beyond our initial perspectives, as I did in the picture above. Sometimes, simply picturing something in a new way can yield helpful insights.
The trick is to apply this sort of thing to thinking critically about consciousness. In this case, it might look like creating metaphors that represent some aspect being studied. Metaphors may help us think about the topic in ways that don’t automatically trigger our biases. Thus, this could help us avoid biases against certain types of solutions, and truly seek whatever the science reveals.